Edited on Dillinger
Leetcode website: Leetcode-Chinese, Leetcode
Leetcode Animation: Github MisterBooo/LeetCodeAnimation, bilibili website
Leetcode Solutions: Github franklingu/leetcode
Tags
链表
数组
- 二分法:二分法模板视频
- 按位与法:
- 56-1 数组中数字出现的次数 Medium
- 动态规划/分治法:
- 53 Maximum Subarray Easy
23. Merge k Sorted Lists
leetcode link Hard
Description: Merge k sorted linked lists and return it as one sorted list. Analyze and describe its complexity.
复杂度分析:
- 一共K条链表,总共有N个节点。
- 暴力法:最暴力的做法是把N个数放到一个数组里,再一起排序。每次比较K个指针的大小O(K),共比较N次。时间复杂度 O(K*N),空间复杂度 O(N)。
- 优先队列法:由于K个链表是有序的,实际上只需要维护K个指针从K个链表的头向尾滑动,每次选取K个链表的表头里的最小加入新的有序链表里。这里可以接用最小堆(优先队列)维护K个链表的当前头位置的值。每次比较K个指针求min,O(logK),一共N次,时间复杂度变为 O(N*logK)。空间复杂度上,看不同的构造最小堆的方式:如果是一开始就把所有N个节点构建最小堆,则是O(N),如果是一边比较K个头指针求min,一边pop后push新的头指针进去,则只需要O(K)。
- 归并排序法(merge sort):首先实现2个有序链表的合并,而后按照归并排序的思路,持续对K个链表进行两两排序,如果是奇数个,则最后一个链表本轮不排序直接进入下一轮,直至最终只剩下一个链表结束。K条链表的总节点数是N,平均每条链表有N/K个节点,因此合并两条链表的时间复杂度是O(N/K)。从K条链表开始两两合并成1条链表,因此每条链表都会被合并logK次,因此总共的时间复杂度是K * logK * N / K,即 O(NlogK)。
\( O(Nlog^K\)- 分治法:递归。
- Solution 1: 暴力法
# Definition for singly-linked list. # class ListNode(object): # def __init__(self, x): # self.val = x # self.next = None class Solution(object): def mergeKLists(self, lists): """ :type lists: List[ListNode] :rtype: ListNode """ if not lists or len(lists)==0: #排除特殊情况 return None if len(lists)==1: return lists[0] node_list = [] #把所有的node全部存入一个列表中 for head in lists: while head: node_list.append(head.val) head = head.next node_list.sort() #列表排序 res_head = ListNode(-1) #新建链表把列表中的node连接起来 cur = res_head for node in node_list: new_node = ListNode(node) cur.next = new_node cur = cur.next return res_head.next- Solution 2: 优先队列
- python heapq documents
class Solution(object): def mergeKLists(self, lists): """ :type lists: List[ListNode] :rtype: ListNode """ if not lists or len(lists)==0: return None if len(lists)==1: return lists[0] import heapq #优先队列 小顶堆 node_heap = [] for head in lists: while head: heapq.heappush(node_heap, head.val) head = head.next dummy = ListNode(None) cur = dummy while node_heap: temp_node = ListNode(heapq.heappop(node_heap)) # 自小顶堆pop出的元素为最小元素 cur.next = temp_node cur = cur.next return dummy.next - Solution 3: 链表版归并排序
class Solution(object): def mergeKLists(self, lists): """ :type lists: List[ListNode] :rtype: ListNode """ def merge2Lists(l_a, l_b): cur = dummy = ListNode(-1) while l_a and l_b: # 当两个链表都没到结尾时 if l_a.val <= l_b.val: cur.next = l_a l_a = l_a.next else: cur.next = l_b l_b = l_b.next cur = cur.next cur.next = l_a if l_a else l_b #其中一个链表到了结尾时,直接append到后面 return dummy.next if not lists or len(lists)==0: #排除特殊情况 return None if len(lists)==1: return lists[0] #类似归并实现k链表的两两排序 while len(lists)>1: #不断进行两两归并 tmp = [] for i in range(len(lists)//2): #0-1, 2-3,4-5,按顺序归并 tmp.append(merge2Lists(lists[2*i], lists[2*i+1])) if len(lists)%2: #如果是奇数个链表,则最后一个链表直接不用合并加上去 tmp.append(lists[-1]) lists = tmp #准备下一次归并 return lists[0]- Solution 4:分治法(递归)

class Solution(object): def merge(self, node_a, node_b): dummy = ListNode(None) cursor_a, cursor_b, cursor_res = node_a, node_b, dummy while cursor_a and cursor_b: # 对两个节点的 val 进行判断,直到一方的 next 为空 if cursor_a.val <= cursor_b.val: cursor_res.next = ListNode(cursor_a.val) cursor_a = cursor_a.next else: cursor_res.next = ListNode(cursor_b.val) cursor_b = cursor_b.next cursor_res = cursor_res.next # 有一方的next的为空,就没有比较的必要了,直接把不空的一边加入到结果的 next 上 if cursor_a: cursor_res.next = cursor_a if cursor_b: cursor_res.next = cursor_b return dummy.next def mergeKLists(self, lists): """ :type lists: List[ListNode] :rtype: ListNode """ length = len(lists) # 边界情况 if length == 0: return None if length == 1: return lists[0] # 分治 mid = length // 2 return self.merge(self.mergeKLists(lists[:mid]), self.mergeKLists(lists[mid:length]))
33. Search in Rotated Sorted Array
leetcode link Medium
Description:

思路分析:
- 参考博客:解决旋转数组问题的通用思想
- N为数组的长度
- 暴力法(Brute Force):采用线性扫描的方式搜索,时间复杂度:O(N),空间复杂度为O(1),使用到的临时变量的个数是常数。
- 二分查找(Binary Search):时间复杂度O(logn)。
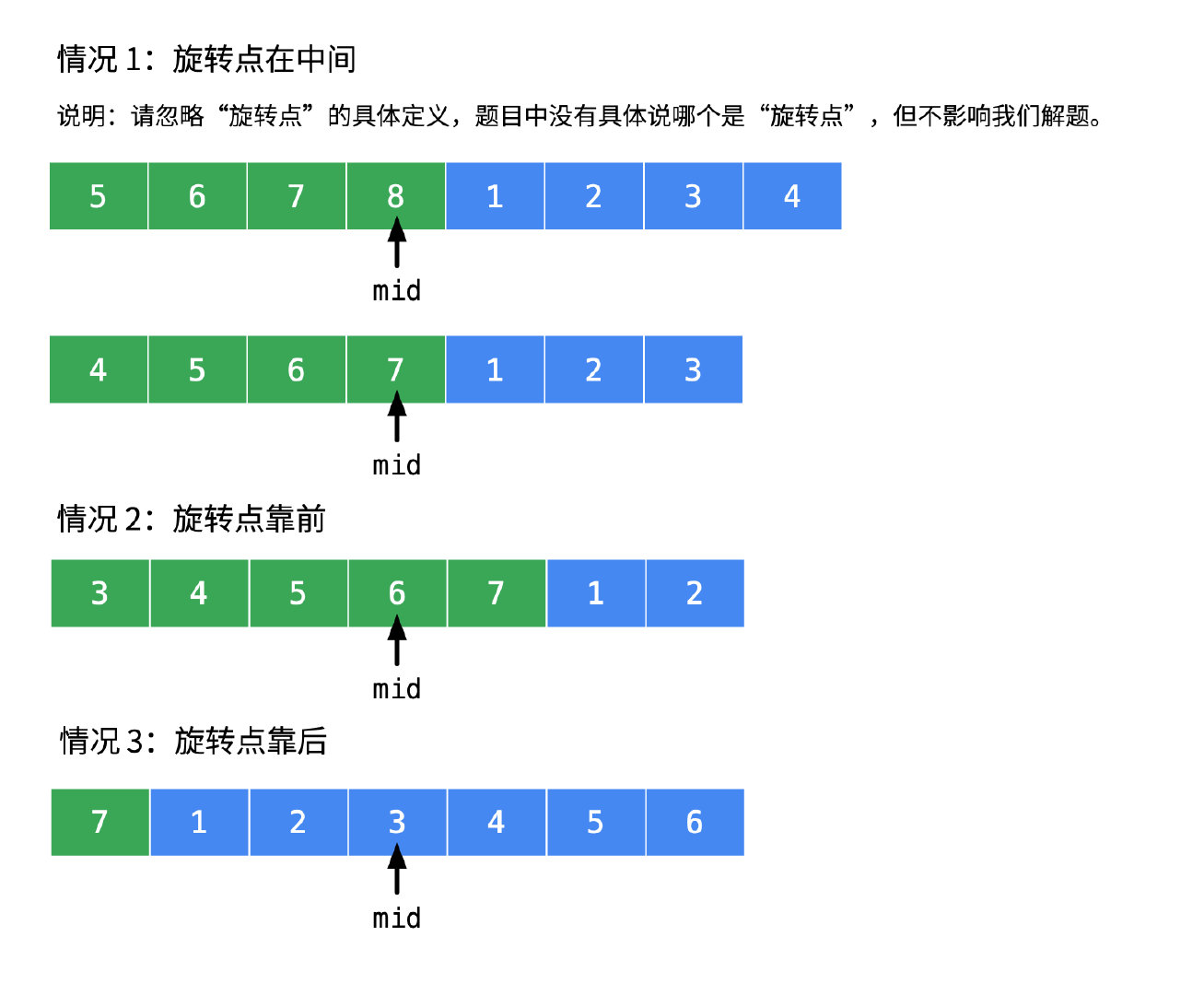
题目中说:假设数组中不存在重复的元素
- 则说明:将搜索区间从中间一分为二,mid一定会落在其中一个有序区间里。 且中间元素把待搜索区间分成了两部分,两部分具有的性质是至少有一部分是有序的。
- 步骤:先根据mid和left判断哪边是有序的。再根据mid和target的值确定target在哪边,进而缩小搜索范围。
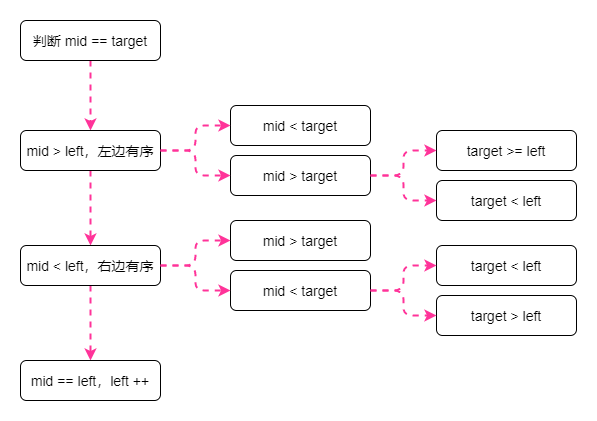
- Solution 1:二分法
class Solution(object): def search(self, nums, target): """ :type nums: List[int] :type target: int :rtype: int """ left, right = 0, len(nums)-1 while left <= right: mid = (left + right)//2 if nums[mid] == target: # 找到了 return mid if nums[left] < nums[mid]: # 左边是有序的 if nums[mid] < target: # target比mid更大,则一定在右边 left = mid + 1 elif nums[mid] > target: if nums[left] <= target: # target更小,但是比left的大,则在mid左边 right = mid - 1 else: # target更小,且比left的小,则在mid右边 left = mid + 1 elif nums[left] > nums[mid]: # 右边是有序的 if nums[mid] > target: # target更小,则一定在左边 right = mid - 1 else: if nums[left] <= target: # target更大,且比left的大,则在左边头部 right = mid - 1 else: # target更大,但是没有left大,mid右半部 left = mid + 1 else: # mid = left, 且无重复,则说明两个指针指向同一个元素了。则真正的target一定是在右边,因为left已经是最左边的元素了。 left = left + 1 return -1同类型题目:
81. Search in Rotated Sorted Array II
leetcode link Medium
Description:

思路分析:
- 参考博客:搜索旋转排序数组 II
- 在33题的基础上,如果left = mid = right,则无法判断往哪边缩区间,因此可以将left 和 right指针同时往内移动。(其实不加这一句也可以,因为33题中已经写了left = left + 1的情况。只是时间复杂度会更高)
-
注意要写成if elif,因为这个操作过后可能会越界(如果输入为[1],0),这时应该直接跳出while循环输出为false。
- Solution 1.
class Solution(object): def search(self, nums, target): """ :type nums: List[int] :type target: int :rtype: int """ left, right = 0, len(nums)-1 while left <= right: mid = (left + right)//2 if nums[mid] == target: # 找到了 return True if nums[left]==nums[mid]==nums[right]: ## 如果是重复数字 left = left + 1 right = right - 1 elif nums[left] < nums[mid]: # 左边是有序的 if nums[mid] < target: # target比mid更大,则一定在右边 left = mid + 1 elif nums[mid] > target: if nums[left] <= target: # target更小,但是比left的大,则在mid左边 right = mid - 1 else: # target更小,且比left的小,则在mid右边 left = mid + 1 elif nums[left] > nums[mid]: # 右边是有序的 if nums[mid] > target: # target更小,则一定在左边 right = mid - 1 else: if nums[left] <= target: # target更大,且比left的大,则在左边头部 right = mid - 1 else: # target更大,但是没有left大,mid右半部 left = mid + 1 else: # mid = left, 且无重复,则说明两个指针指向同一个元素了。则真正的target一定是在右边,因为left已经是最左边的元素了。 left = left + 1 return False
153. Find Minimum in Rotated Sorted Array
leetcode link Medium
Description:

思路分析:
- 参考博客: 寻找旋转排列数组中的最小值
-
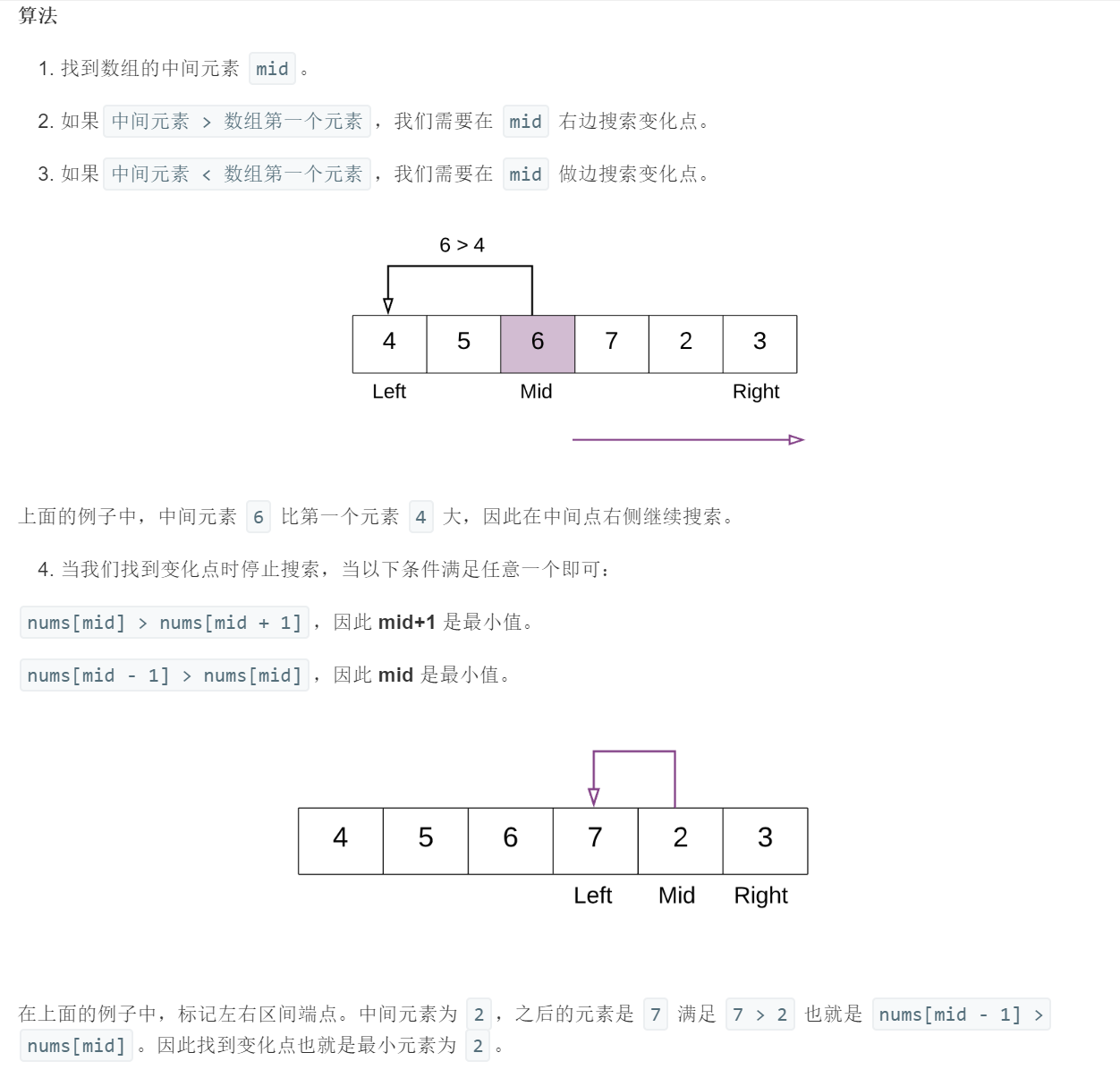
- Solution 1:
class Solution(object): def findMin(self, nums): """ :type nums: List[int] :rtype: int """ # If the list has just one element then return that element. if len(nums) == 1: return nums[0] # left pointer left = 0 # right pointer right = len(nums) - 1 # if the last element is greater than the first element then there is no rotation. # e.g. 1 < 2 < 3 < 4 < 5 < 7. Already sorted array. # Hence the smallest element is first element. A[0] if nums[right] > nums[0]: return nums[0] # Binary search way while right >= left: # Find the mid element mid = left + (right - left) / 2 # if the mid element is greater than its next element then mid+1 element is the smallest # This point would be the point of change. From higher to lower value. if nums[mid] > nums[mid + 1]: return nums[mid + 1] # if the mid element is lesser than its previous element then mid element is the smallest if nums[mid - 1] > nums[mid]: return nums[mid] # if the mid elements value is greater than the 0th element this means # the least value is still somewhere to the right as we are still dealing with elements greater than nums[0] if nums[mid] > nums[0]: left = mid + 1 # if nums[0] is greater than the mid value then this means the smallest value is somewhere to the left else: right = mid - 1
1095. Find in Mountain Array
leetcode link Hard
Description:

思路分析:
- 参考博客:山脉数组中查找目标值
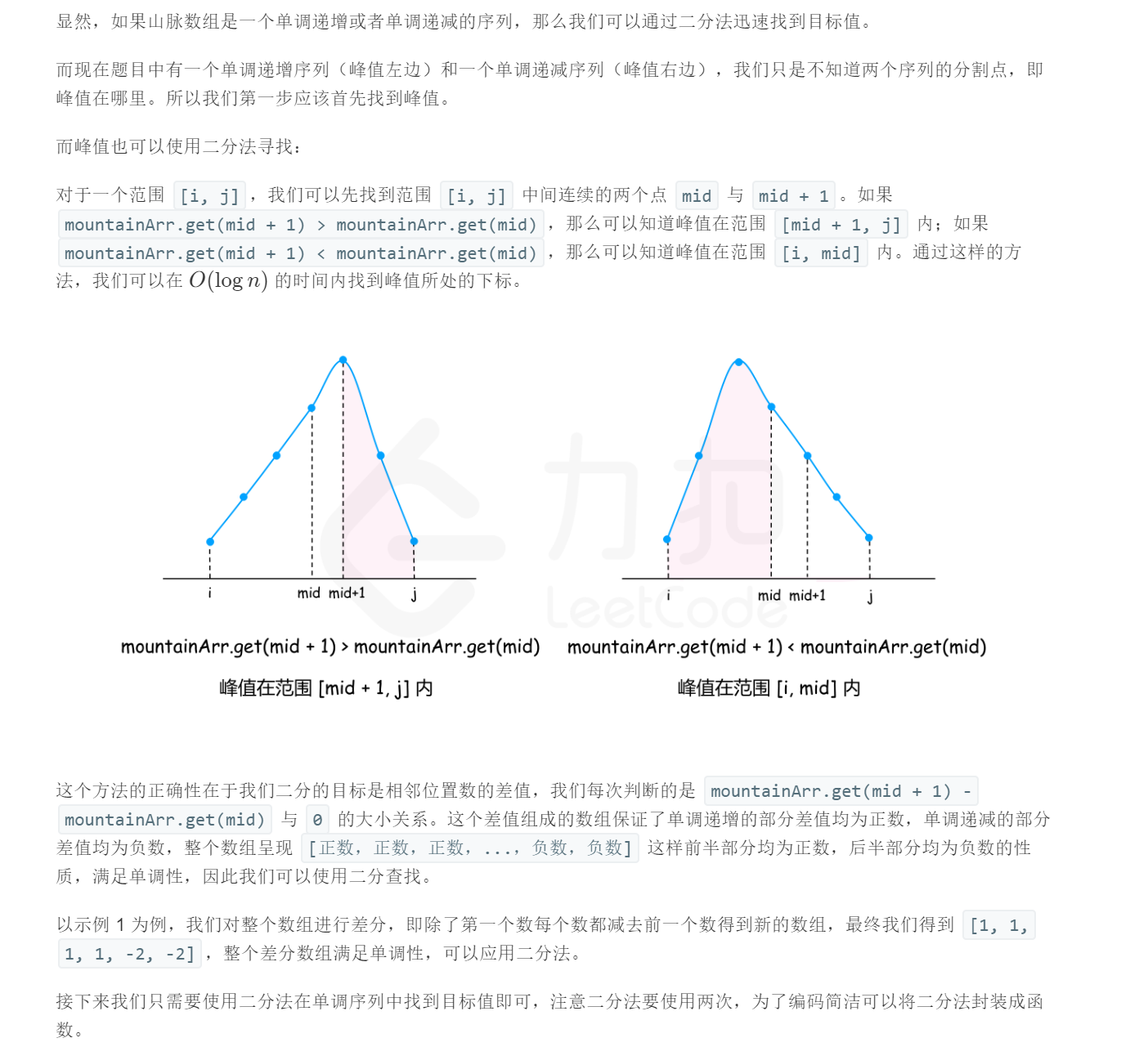
- 算法:
- 先使用二分法找到数组的峰值。
- 在峰值左边使用二分法寻找目标值。
- 如果峰值左边没有目标值,那么使用二分法在峰值右边寻找目标值。
- 复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(logn),进行了三次二分搜索,每次的时间复杂度都为O(logn)。
- 空间复杂度:O(1),只需要常数的空间存放若干变量。
- Solution 1: (no time exceeded)
def binary_search(mountain, target, l, r, key=lambda x: x): target = key(target) while l <= r: mid = (l + r) // 2 cur = key(mountain.get(mid)) if cur == target: return mid elif cur < target: l = mid + 1 else: r = mid - 1 return -1 class Solution: def findInMountainArray(self, target, mountain_arr): l, r = 0, mountain_arr.length() - 1 while l < r: mid = (l + r) // 2 if mountain_arr.get(mid) < mountain_arr.get(mid + 1): l = mid + 1 else: r = mid peak = l index = binary_search(mountain_arr, target, 0, peak) if index != -1: return index index = binary_search(mountain_arr, target, peak + 1, mountain_arr.length() - 1, lambda x: -x) return index - My Solution(time exceded, need to improve)
class Solution(object): def findInMountainArray(self, target, mountain_arr): """ :type target: integer :type mountain_arr: MountainArray :rtype: integer """ def findMountainPeak(input_arr, left, right): mid = left + (right - left)//2 while left < right: if input_arr.get(mid) < input_arr.get(mid+1): left = mid + 1 else: right = mid return left def findMountrainLeft(input_arr, target, left, right): mid = left + (right - left)//2 cur = input_arr.get(mid) while left <= right: if cur == target: return mid elif cur < target: left = mid + 1 else: right = mid - 1 return -1 def findMountrainReverse(input_arr, target, left, right): mid = left + (right - left)//2 cur = input_arr.get(mid) while left <= right: if cur == target: return mid elif cur < target: right = mid - 1 else: left = mid + 1 return -1 length = mountain_arr.length() peakindex = findMountainPeak(mountain_arr, 0, length-1) peak_value = mountain_arr.get(peakindex) if peak_value == target: return peakindex elif peak_value < target: # 如果峰值都比target小,则无需再找了 return -1 else: cur_index = findMountrainLeft(mountain_arr, target, 0, peakindex-1) if cur_index == -1: return -1 else: return findMountrainReverse(mountain_arr, target, peakindex, length-1)
56-1. 数组中数字出现的次数
leetcode link Medium
Description:

思路分析:
- 参考博客:数组中数字出现的次数——位运算
简单入门:一个只出现一次的数字 除了一个数字出现依次,其他都出现了两次,找到出现一次的数 全员异或即可
class Solution:
def singleNumber(self, nums):
single_number = 0
for num in nums:
single_number ^= num
return single_number
- 两个数字出现一次
- 任何数和本身异或为0。参考以上的解法,可以把这两个不同的数字分成A和B两组。
- 分组满足两个条件:
- 两个只出现一次的数字在不同的组中;
- 相同的数字会被分到相同的组中。
- 这样A、B两个组分别组内全员异或则可以得到那两个只出现一次的数字。
- 分组方法:
- 取在全部数字异或后,值为1的那一位。因为这一位除了两个不同的数字外其他的异或后都为0了,最后值为1说明对于这一位来说,两个数字是不同的,所以可以作为分类依据。
- 复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(N),其中N为数组长度,我们只需要遍历数组两次。
- 空间复杂度为O(1),只需要常数的空间存放若干变量。
- Solution 1. 分组异或
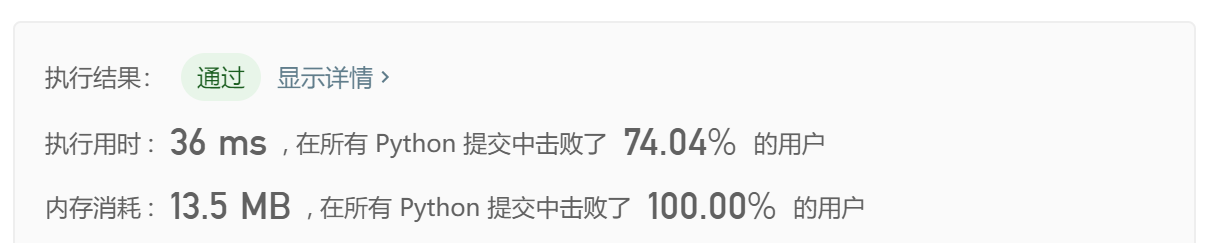
class Solution(object): def singleNumbers(self, nums): """ :type nums: List[int] :rtype: List[int] """ res = 0 # 存放所有数字异或后的结果 a = 0 b = 0 for num in nums: res ^= num # 找到第一位不是零的作为分组依据 h = 1 while (res & h) == 0: h <<= 1 #二进制左移一位 print for num in nums: # 根据该位是否为0分成两组 if (h & num) == 0: a ^= num else: b ^= num return [a, b]
53. Maximum Subarray
**
leetcode link Easy
Description:

思路分析:
-
Reference: 四种方法 暴力法、动态规划、贪心、分治法,线段树。
- Solution 1 Greedy:
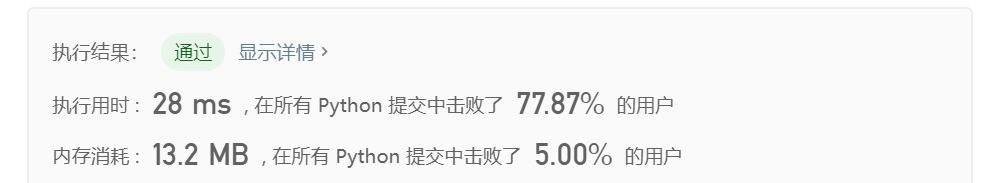
class Solution(object): def maxSubArray(self, nums): """ :type nums: List[int] :rtype: int """ # greedy 也是动态规划的简化版,因为f(i)仅与f(i-1有关) length = len(nums) pre_sum = nums[0] max_sum = nums[0] for i in range(1, length): # 遍历一次数组,看之前计算的连续和是否为负数 if pre_sum<0: pre_sum = nums[i] # 如果是则说明对当前的数字无增益,则从该数字开始重新计算连续和 else: pre_sum = pre_sum + nums[i] # 如果之前计算的连续和为正数,则加过来为当前数字增益 max_sum = max(max_sum, pre_sum) # 每次循环都更新最大连续和的值 return max_sumor more simplyfied
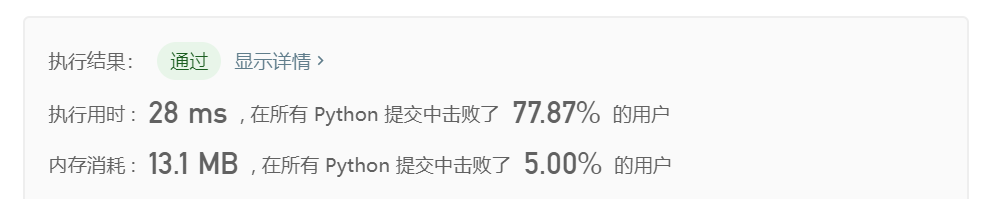
class Solution(object): def maxSubArray(self, nums): """ :type nums: List[int] :rtype: int """ # greedy 也是动态规划的简化版,因为f(i)仅与f(i-1有关) pre_sum = nums[0] max_sum = nums[0] for i in range(1, len(nums)): # 遍历一次数组,看之前计算的连续和是否为负数 pre_sum = max(pre_sum + nums[i], nums[i]) max_sum = max(max_sum, pre_sum) # 每次循环都更新最大连续和的值 return max_sum - 复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(N),其中 N为 nums 数组的长度。我们只需要遍历一遍数组即可求得答案。
- 空间复杂度:O(1)。我们只需要常数空间存放若干变量。
- Solution 2 动态规划:
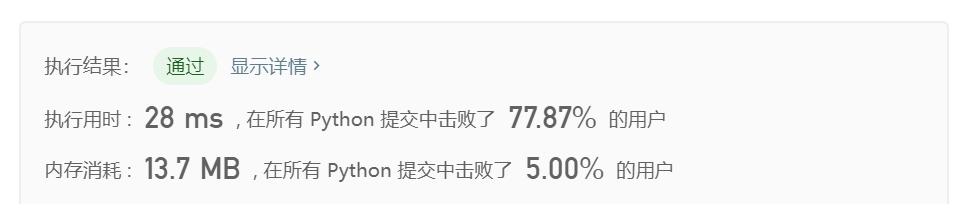
class Solution(object): # f[i]代表以nums[i]结尾的最大子序列和 # f[i] 等于 f[i-1]+a[i]、a[i]二者最大值 # 空间复杂度为n,时间复杂度为n def maxSubArray(self, nums): """ :type nums: List[int] :rtype: int """ f = [nums[0]] for i in range(1, len(nums)): # 遍历一次数组,看之前计算的连续和是否为负数 f.append(max(nums[i], f[-1]+nums[i])) return max(f) - Solution 3 分治法:

class Solution(object): def maxSubArray(self, nums): """ :type nums: List[int] :rtype: int """ def max_struct(nums): n = len(nums) #递归终止条件 if n == 1: elem = nums[0] return elem,elem,elem,elem else: #递归计算左半边最大子序和 l_max_left, l_max_right, l_max_mid, l_i_sum = max_struct(nums[0:len(nums) // 2]) #递归计算右半边最大子序和 r_max_left, r_max_right, r_max_mid, r_i_sum = max_struct(nums[len(nums) // 2:len(nums)]) max_left = max(l_max_left, l_i_sum + r_max_left) max_right = max(r_max_right, r_i_sum + l_max_right) max_mid = max(l_max_mid, r_max_mid, l_max_right + r_max_left) ## 易错点! i_sum = l_i_sum + r_i_sum return max_left, max_right, max_mid, i_sum m_left, m_right, m_mid, i_sum = max_struct(nums) return max(m_left, m_right, m_mid)- 复杂度分析:
 —
—
- 复杂度分析:
